搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“AGB”相关记录36条 . 查询时间(0.249 秒)

IRC+10216 (CW Leo) 是距离我们最近的富碳(C/O > 1)渐近巨星(AGB星),天文学家在其星周包层中已探测到106 种不同的分子种类(不含同位素),因此这颗AGB星是星际空间中名副其实的“分子工厂”。之前,人们已发表过使用各类射电望远镜对IRC+10216星周分子的观测结果,但未见有在3mm波段的全波段谱线巡测结果。
Forest Total and Component Above-Ground Biomass (AGB) Estimation through C- and L-band Polarimetric SAR Data
total and component biomass backscatter polarimetric SAR
2023/12/8
Forest biomass plays an essential role in forest carbon reservoir studies, biodiversity protection, forest management, and climate change mitigation actions. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), especially...
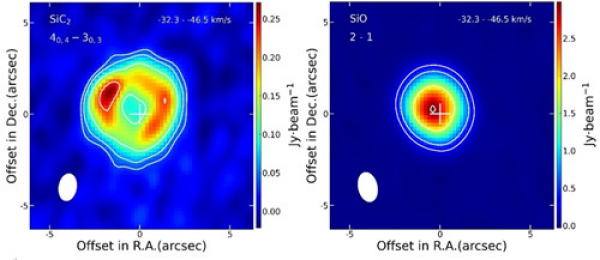
中国科学院新疆天文台利用ALMA观测到二碳化硅在富碳AGB星周呈环状分布(图)
ALMA 二碳化硅 富碳AGB星 环状分布
2023/10/16
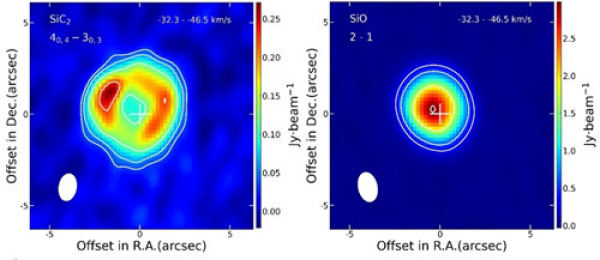
中国科学院新疆天文台利用ALMA观测到二碳化硅在富碳AGB星周呈环状分布.(图)
新疆天文台 观测 二碳化硅 恒星演化
2023/10/25
渐近巨星支(Asymptotic Giant Branch,AGB)恒星的星周包层(Circumstellar Envelope,CSE)中含有大量气体分子(已探测到105个),约占星际空间发现的所有分子(超300个)的三分之一。研究星周包层中分子的物理及化学特征,对探讨恒星演化具有重要意义。气体和尘埃是星周包层的重要组成部分。二碳化硅(SiC2)分子是富碳AGB星周尘埃颗粒的主要成分之一。SiC...
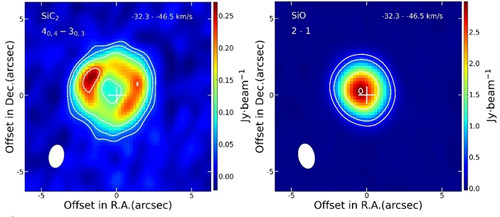
渐近巨星支(Asymptotic Giant Branch, AGB)恒星的星周包层(Circumstellar Envelope,CSE)中含有大量气体分子(已探测到105个),约占星际空间发现的所有分子(超300个)的三分之一。研究星周包层中分子的物理以及化学特征对研究恒星演化具有重要意义。气体和尘埃是星周包层的重要组成部分,二碳化硅(SiC2)分子是富碳AGB星周尘埃颗粒的主要成分之一。Si...
AGB Estimation in a Tropical Mountain Forest (TMF) by Means of RGB and Multispectral Images Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
forest AGB UAV RGB data multispectral data
2024/2/4
The present investigation evaluates the accuracy of estimating above-ground biomass (AGB) by means of two different sensors installed onboard an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) platform (DJI Inspire I) ...
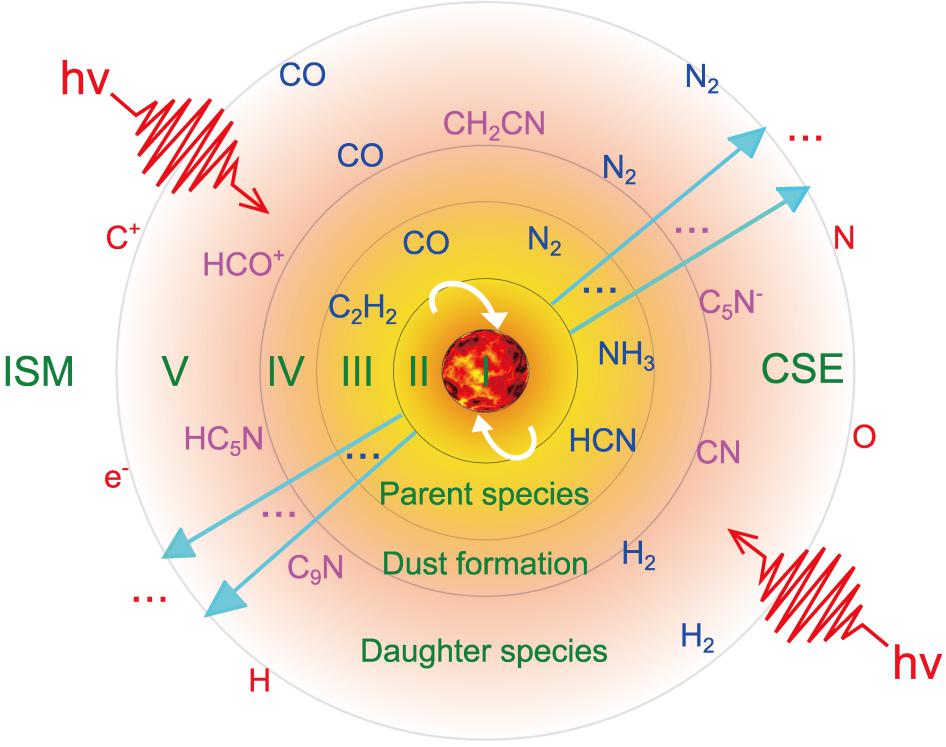
近日,一项关于c-SiC3等含硅分子在渐近巨星分支(AGB)恒星IRC+10216星周的形成机理的研究结果发表于《美国国家科学院院刊》。该成果是原子分子与化学动力学实验、量化计算、天体化学模拟强强联合、共同攻关的一个典型例子,展示了天体化学这门新兴学科“高度交叉融合”的本质特点。此项工作由华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室研究员杨涛、中国科学院新疆天文台天体化学团组研究员李小虎,及美国加...
Infrared two-colour diagrams for AGB stars using AKARI, MSX, IRAS and NIR data
stars: AGB and post-AGB - circumstellar matter - infrared: stars - dust extinction - radiative transfer
2011/10/12
Using a revised version of the catalog of AGB stars by Suh & Kwon (2009), we present various infrared two-colour diagrams (2CDs) for 3003 O-rich, 1168 C-rich, 362 S-type and 35 silicate carbon stars i...
The First Fluorine Abundance Determinations in Extragalactic AGB Carbon Stars
FluorineAbundance Determinations Extragalactic
2011/9/29
Fluorine (19F) abundances (or upper limits) are derived in six extragalactic AGB carbon stars from the HF(1-0) R9 line at 2.3358 mu in high resolution spectra. The stars belong to the Local Group gala...
We have conducted an LTE abundance analysis for SAO 40039 a warm post-AGB star whose spectrum is known to show surprisingly strong He I lines for its effective temperature and has been suspected of be...
Characteristics of convection and overshooting in RGB and AGB stars
RGB and AGB stars: convection of stars: turbulent convection model: con-vective overshooting
2011/9/28
Based on the turbulent convection model (TCM) of Li & Yang (2007), we have studied the characteristics of turbulent convection in the envelopes of 2 and 5M stars at the RGB and AGB phases. The TCM has...
We present results of a survey of post-asymptotic giant branch stars (post-AGBs) at high galactic latitude. To date, few post-AGB stars are known throughout the Galaxy and the number of known members ...
The connection between missing AGB stars and extended horizontal branches
missing AGB stars extended horizontal branches
2011/1/13
Recent surveys confirm early results about a deficiency or even absence of CN-strong stars on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) of globular clusters (GCs), although with quite large cluster-to-cluster...
Dust at sub-solar metallicity: the case of post-AGB stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud
Dust at sub-solar metallicity Large Magellanic Cloud
2010/11/11
Low- and intermediate-mass stars are one of the important dust sources in the interstellar medium (ISM) of galaxies. The compositions of dust ejected from these stars are likely to affect those in the...
The dust formed in extended circumstellar envelopes of long-period variables and Miras has a strong influence on the envelope dynamics. A radiatively driven instability caused by the formation of dust...


